RxJS.Observable
- Package
- purescript-rxps
- Repository
- LukaJCB/purescript-rxps
#ObservableImpl Source
data ObservableImpl :: Type -> TypeInstances
Monoid (ObservableImpl a)Functor ObservableImplApply ObservableImplApplicative ObservableImplBind ObservableImplMonad ObservableImplSemigroup (ObservableImpl a)Alt ObservableImplPlus ObservableImplAlternative ObservableImplMonadZero ObservableImplMonadPlus ObservableImplMonadError Error ObservableImplMonadThrow Error ObservableImpl
#ObservableT Source
newtype ObservableT m aConstructors
ObservableT (m (ObservableImpl a))
Instances
(Functor f) => Functor (ObservableT f)(Apply f) => Apply (ObservableT f)(Applicative f) => Applicative (ObservableT f)(Apply f) => Semigroup (ObservableT f a)(Applicative f) => Monoid (ObservableT f a)(Apply f) => Alt (ObservableT f)(Applicative f) => Plus (ObservableT f)(Monad m) => Bind (ObservableT m)(Monad m) => Monad (ObservableT m)(Monad m) => Alternative (ObservableT m)(Monad m) => MonadZero (ObservableT m)(Monad m) => MonadPlus (ObservableT m)
#Observable Source
type Observable a = ObservableT Identity a#runObservableT Source
runObservableT :: forall a m. ObservableT m a -> m (ObservableImpl a)#combineLatest3 Source
combineLatest3 :: forall f d c b a. Apply f => (a -> b -> c -> d) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f c -> ObservableT f dAn Observable of projected values from the most recent values from each input Observable.

#combineLatest Source
combineLatest :: forall f c b a. Apply f => (a -> b -> c) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f cAn Observable of projected values from the most recent values from each input

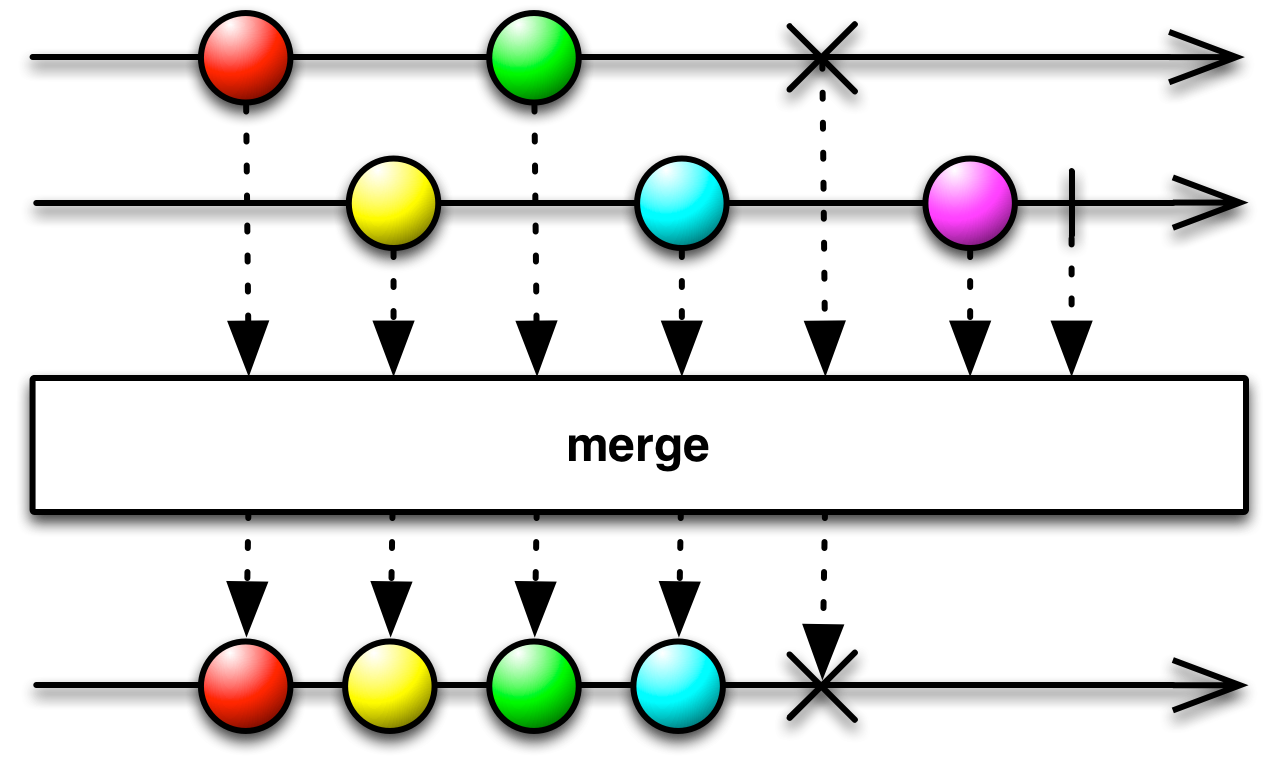
#merge Source
merge :: forall f a. Apply f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aCreates an output ObservableImpl which concurrently emits all values from each input ObservableImpl.
#throw Source
throw :: forall f a. Applicative f => Error -> ObservableT f aCreates an ObservableImpl that immediately sends an error notification.
#just Source
just :: forall f a. Applicative f => a -> ObservableT f aCreates an ObservableImpl that emits the value specify,
and then emits a complete notification. An alias for of.
#never Source
never :: forall f a. Applicative f => ObservableT f aCreates an ObservableImpl that emits no items. Subscriptions it must be
disposed manually.

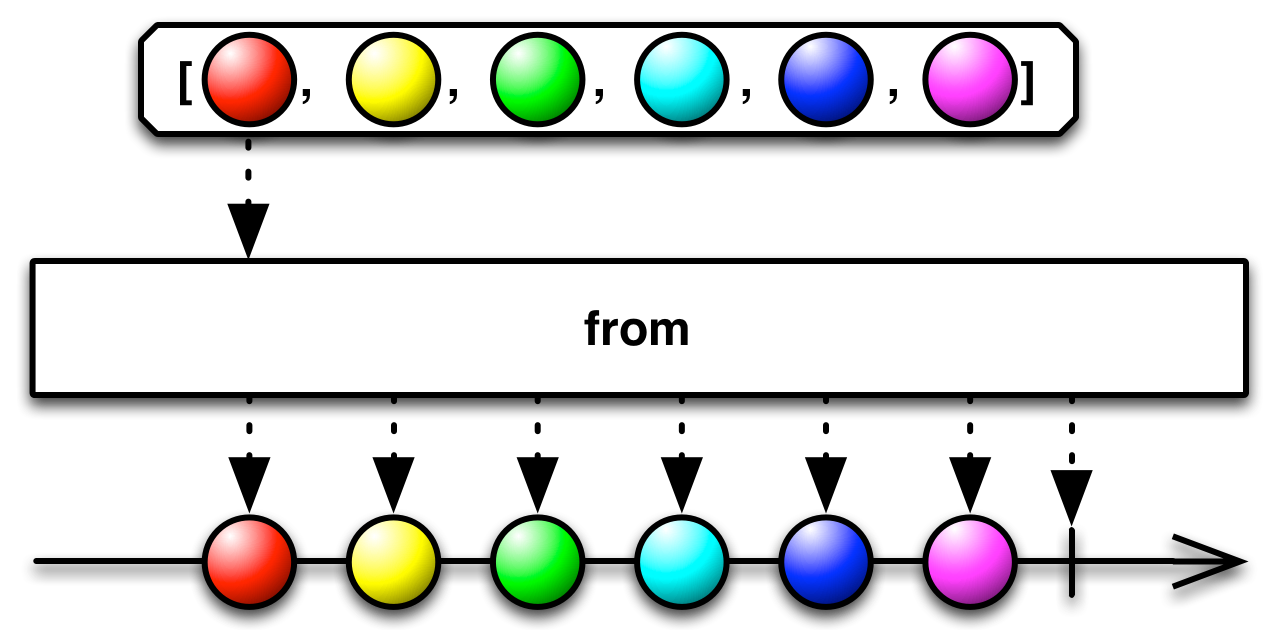
#fromArray Source
fromArray :: forall f a. Applicative f => Array a -> ObservableT f aCreates an ObservableImpl from an Array.

#fromEvent Source
fromEvent :: forall e. EventTarget -> EventType -> ObservableT (Eff (dom :: DOM | e)) EventCreates an ObservableImpl that emits events of the specified type coming from the given event target.
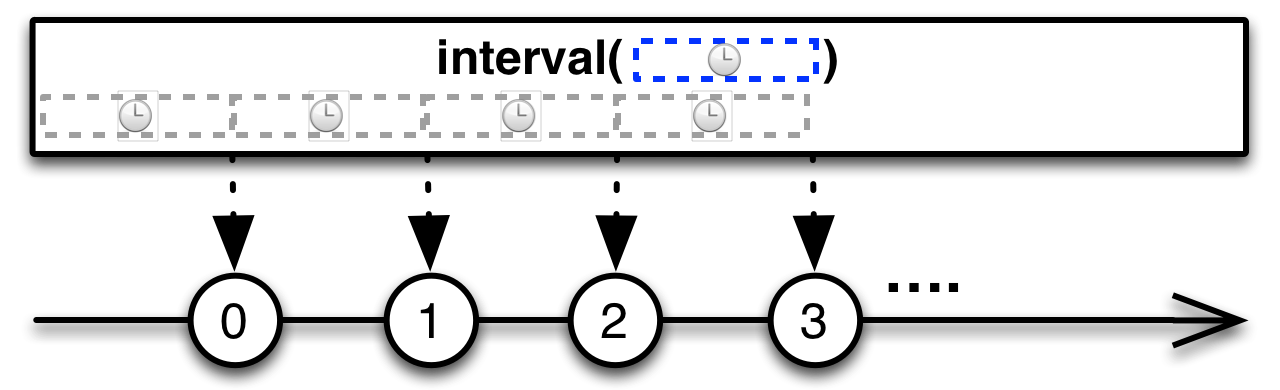
#interval Source
interval :: forall f. Applicative f => Int -> ObservableT f IntReturns an ObservableImpl that emits an infinite sequence of ascending
integers, with a constant interval of time of your choosing between those
emissions.
#range Source
range :: forall f. Applicative f => Int -> Int -> ObservableT f IntThe range operator emits a range of sequential integers, in order, where
you select the start of the range and its length

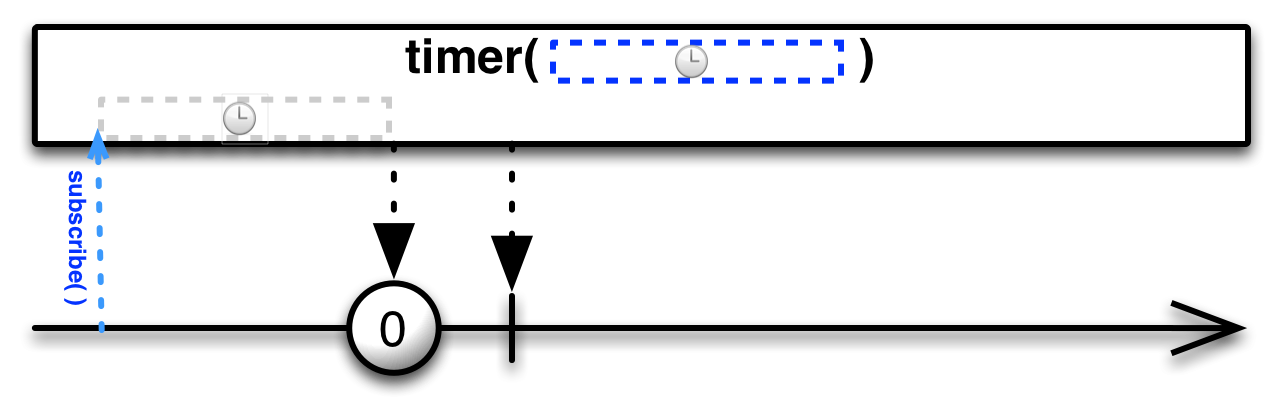
#timer Source
timer :: forall f. Applicative f => Int -> Int -> ObservableT f IntCreates an Observable that, upon subscription, emits and infinite sequence of ascending integers,
after a specified delay, every specified period. Delay and period are in
milliseconds.
#create Source
create :: forall u e a. (Subscriber a -> Eff e u) -> ObservableT (Eff e) a#buffer Source
buffer :: forall f b a. Apply f => ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (Array a)Collects values from the first Observable into an Array, and emits that array only when
second Observable emits.

#bufferCount Source
bufferCount :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (Array a)Collects values from the past as an array, emits that array when
its size (arg1) reaches the specified buffer size, and starts a new buffer.
The new buffer starts with nth (arg2) element of the Observable counting
from the beginning of the last buffer.

#bufferTime Source
bufferTime :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> Int -> Int -> (ObservableT f a) -> (ObservableT f (Array a))Collects values from the past as an array, and emits those arrays periodically in time. The first argument is how long to fill the buffer. The second argument is specifies when to open the next buffer following an emission. The third argument is the maximum size of any buffer.
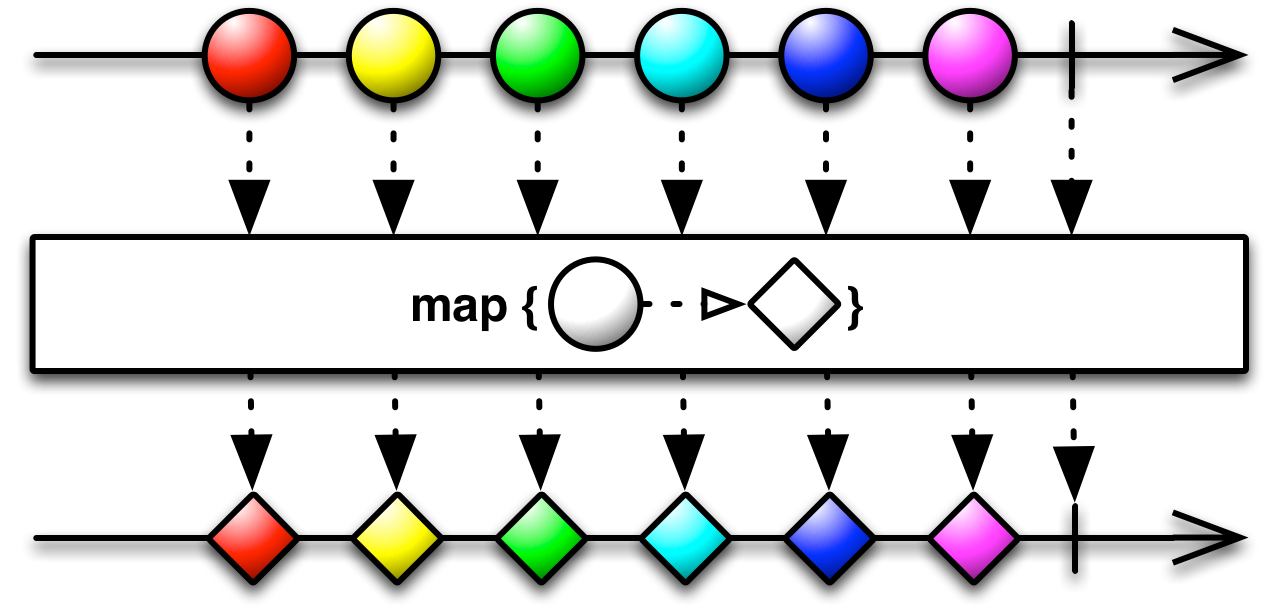
#mapTo Source
mapTo :: forall f b a. Functor f => b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f bEmits the given constant value on the output Observable every time
the source Observable emits a value.
#pairwise Source
pairwise :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (Tuple a a)Puts the current value and previous value together as an array, and emits that.

#partition Source
partition :: forall f a. Applicative f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> Tuple (ObservableT f a) (ObservableT f a)Given a predicate function (arg1), and an Observable (arg2), it outputs a
two element array of partitioned values
(i.e., [ Observable valuesThatPassPredicate, Observable valuesThatFailPredicate ]).

#mergeMap Source
mergeMap :: forall m b a. Monad m => ObservableT m a -> (a -> ObservableT m b) -> ObservableT m bMaps each value to an Observable, then flattens all of these Observables
using mergeAll. It's just monadic bind.

#mergeMapTo Source
mergeMapTo :: forall m b a. Apply m => ObservableT m a -> ObservableT m b -> ObservableT m bMaps each value of the ObservableImpl (arg1) to the same inner ObservableImpl (arg2),
then flattens the result.

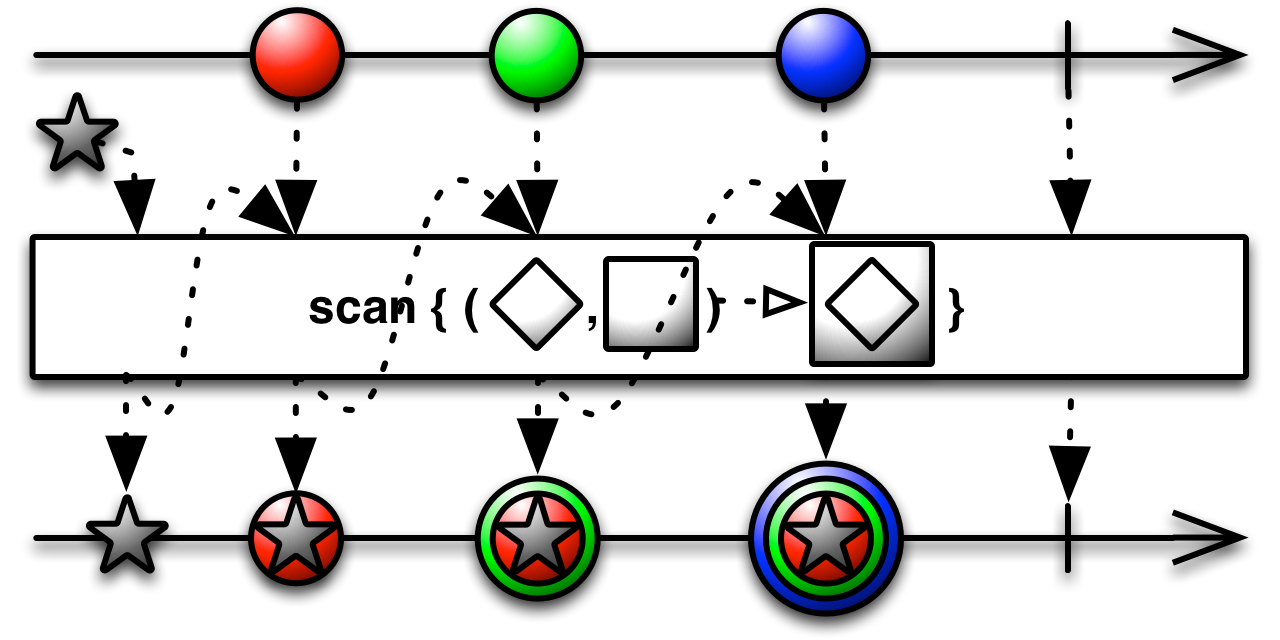
#scan Source
scan :: forall f b a. Functor f => (a -> b -> b) -> b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f bGiven an accumulator function (arg1), an initial value (arg2), and
a source ObservableImpl (arg3), it returns an ObservableImpl that emits the current
accumlation whenever the source emits a value.
#scanM Source
scanM :: forall f m b a. Functor f => Monad m => (a -> b -> m b) -> b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (m b)Same as scan except that its result is encapsulated in a monad.
#debounceTime Source
debounceTime :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aIt's like delay, but passes only the most recent value from each burst of emissions.
#distinct Source
distinct :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable
that are distinct by comparison from previous items.

#distinctUntilChanged Source
distinctUntilChanged :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits all items emitted by the source Observable
that are distinct by comparison from the previous item.

#elementAt Source
elementAt :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aEmits the single value at the specified index in a sequence of emissions from the source
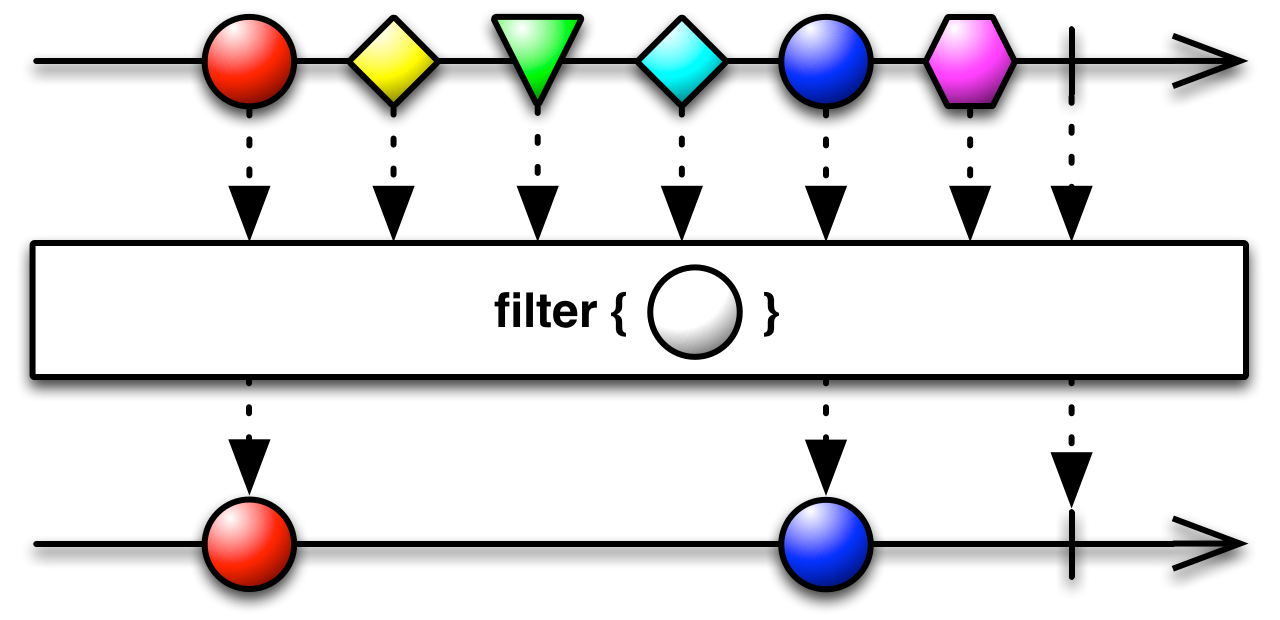
#filter Source
filter :: forall f a. Functor f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aFilter items emitted by the source Observable by only emitting those that
satisfy a specified predicate.
#ignoreElements Source
ignoreElements :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aIgnores all items emitted by the source Observable and only passes calls of complete or error.

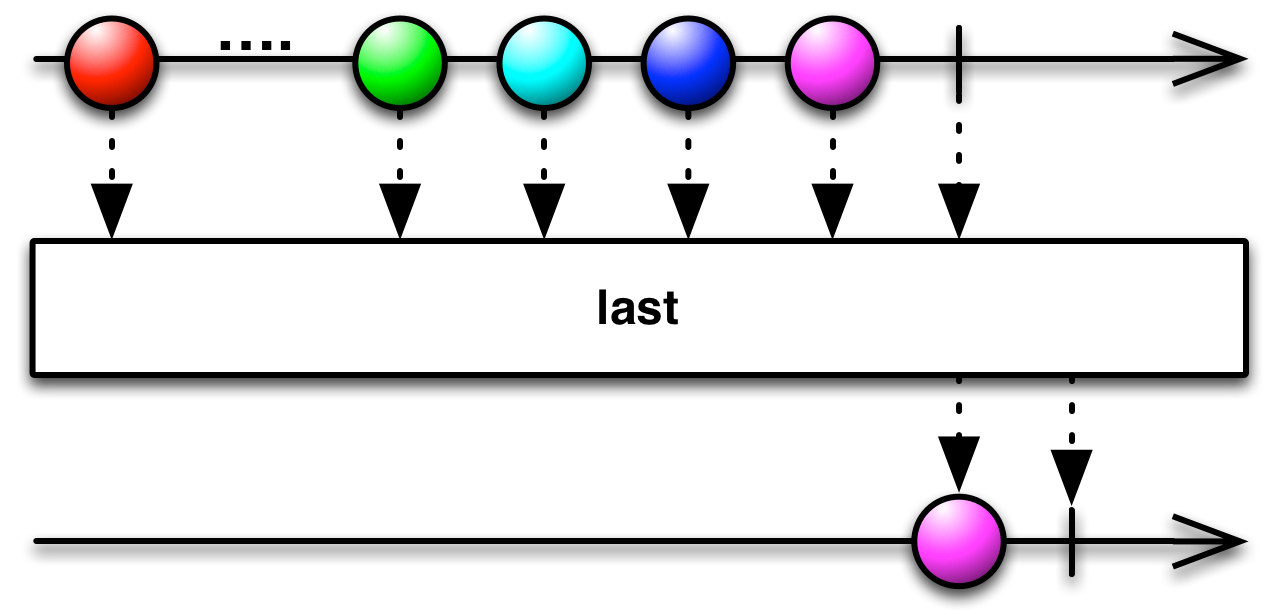
#last Source
last :: forall f a. Functor f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source
Observable that that satisfies the given predicate.
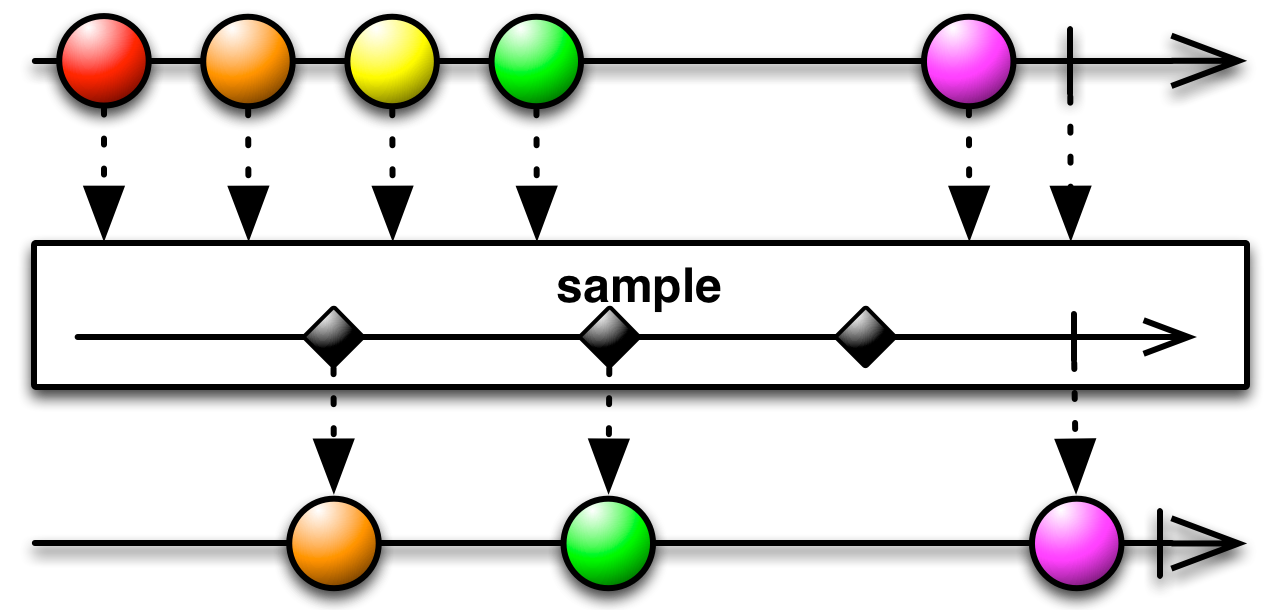
#sample Source
sample :: forall f b a. Apply f => ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aIt's like sampleTime, but samples whenever the notifier Observable emits something.
#sampleTime Source
sampleTime :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aPeriodically looks at the source Observable and emits whichever value it has most recently emitted since the previous sampling, unless the source has not emitted anything since the previous sampling.
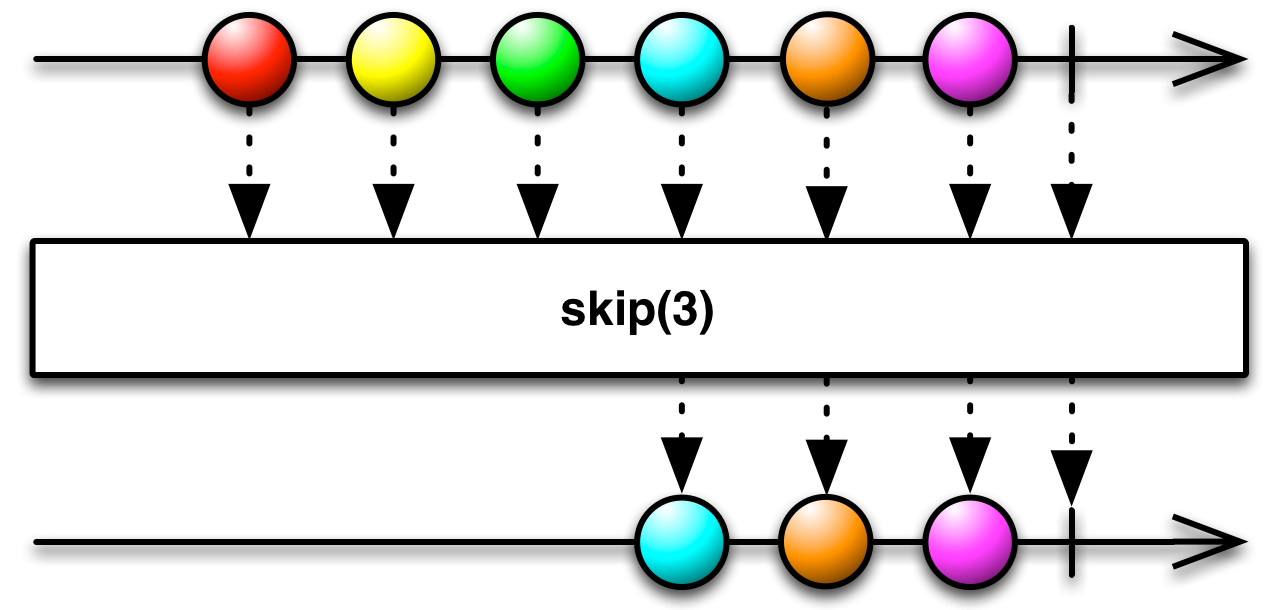
#skip Source
skip :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that skips n items emitted by an
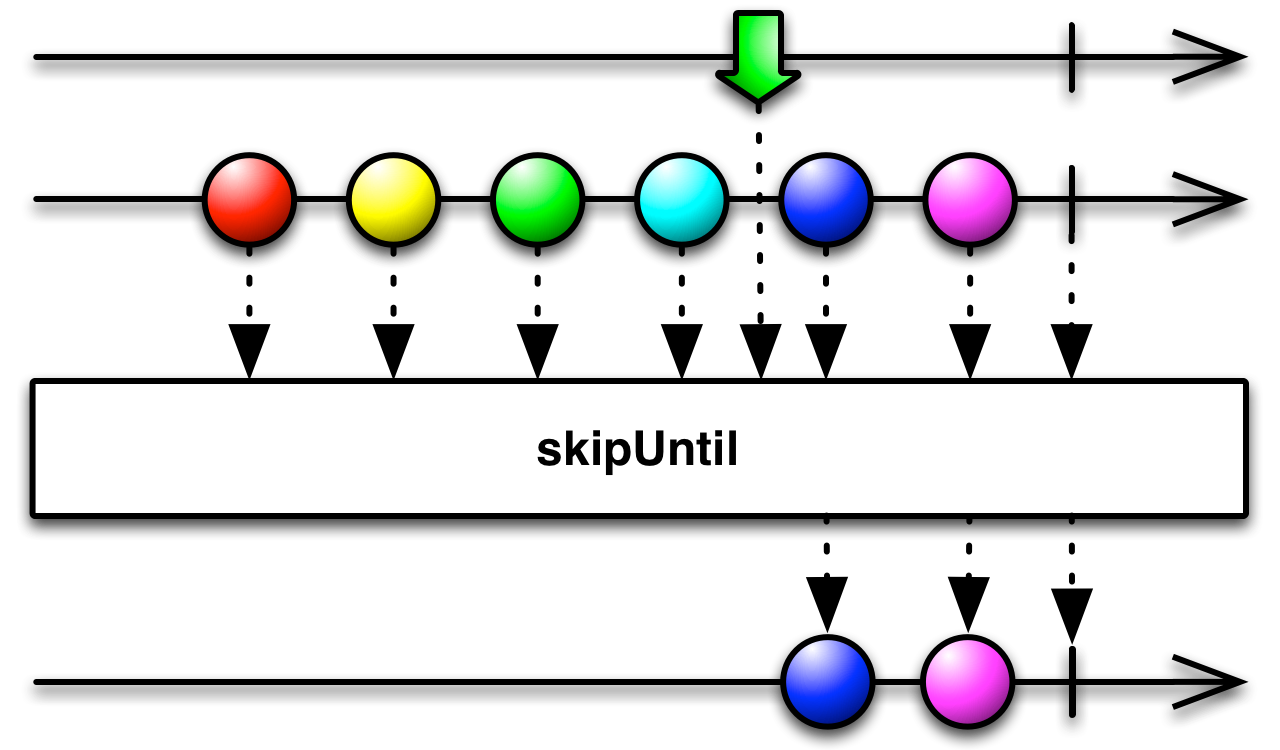
#skipUntil Source
skipUntil :: forall f b a. Apply f => ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
#skipWhile Source
skipWhile :: forall f a. Functor f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that skips all items emitted
by the source Observable as long as a specified condition holds true,
but emits all further source items as soon as the condition becomes false.
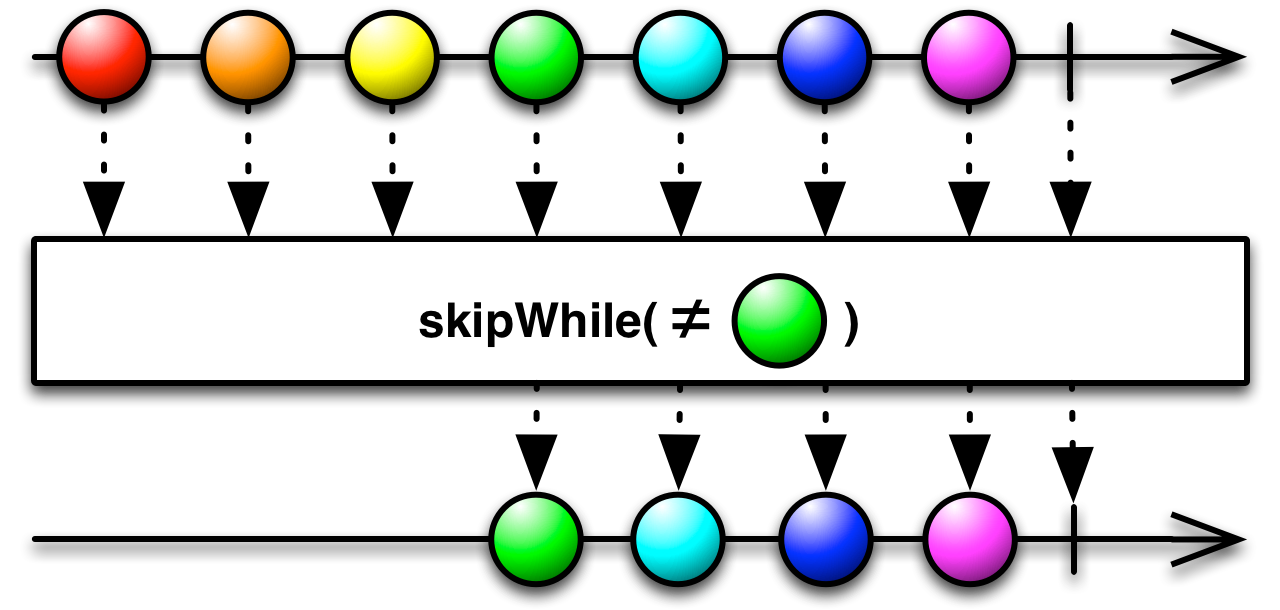
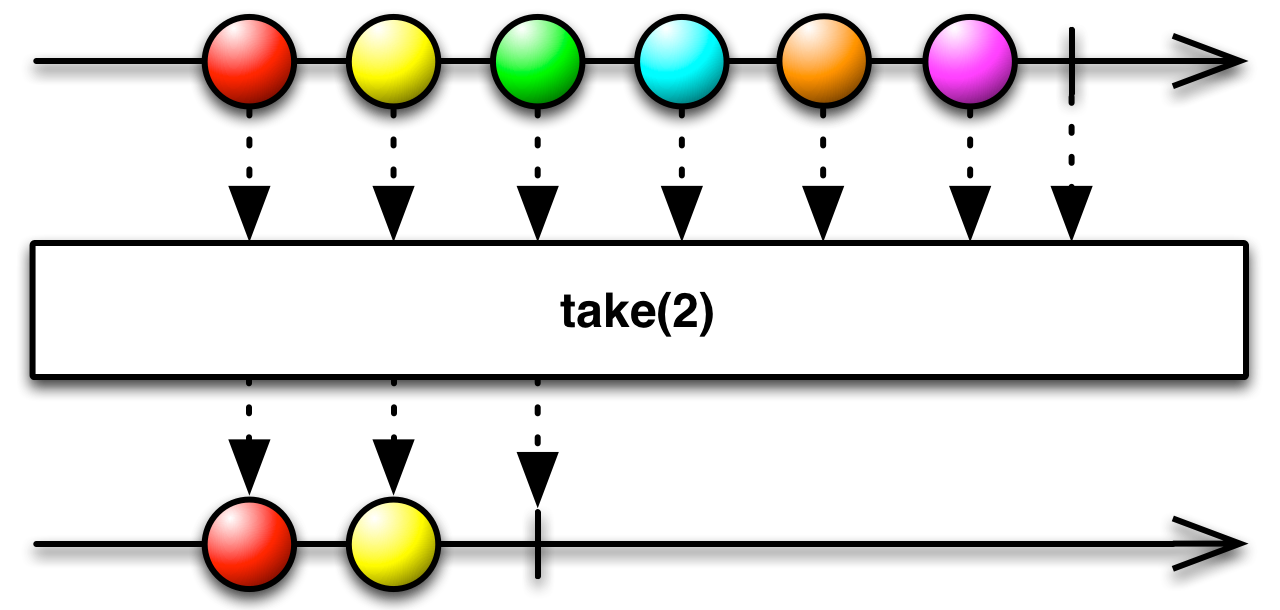
#take Source
take :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aEmits only the first n values emitted by the source
#takeUntil Source
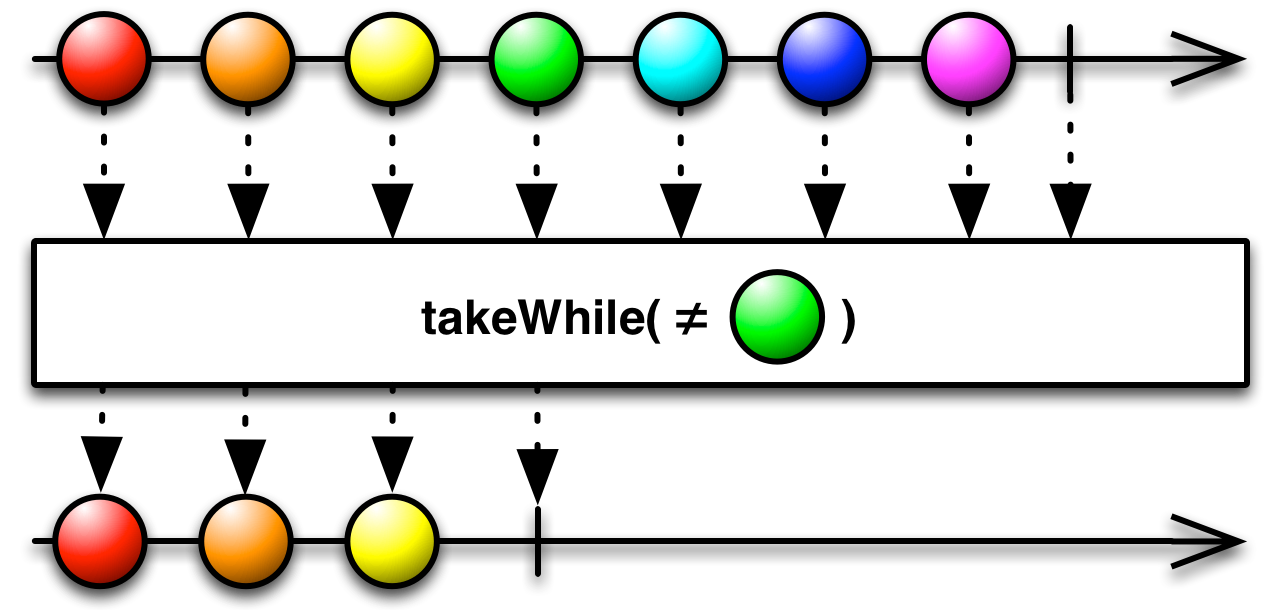
takeUntil :: forall f b a. Apply f => ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aLets values pass until a second Observable emits something. Then, it completes.  -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aEmits values emitted by the source Observable so long as each value satisfies
the given predicate, and then completes as soon as this predicate is not satisfied.
#auditTime Source
auditTime :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aIgnores source values for duration milliseconds,
then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.

#throttleTime Source
throttleTime :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aEmits a value from the source Observable, then ignores subsequent source values
for duration milliseconds, then repeats this process.
#startWithMany Source
startWithMany :: forall m a f. Foldable f => Functor m => f a -> ObservableT m a -> ObservableT m aReturns an Observable that emits the items in the given Foldable before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
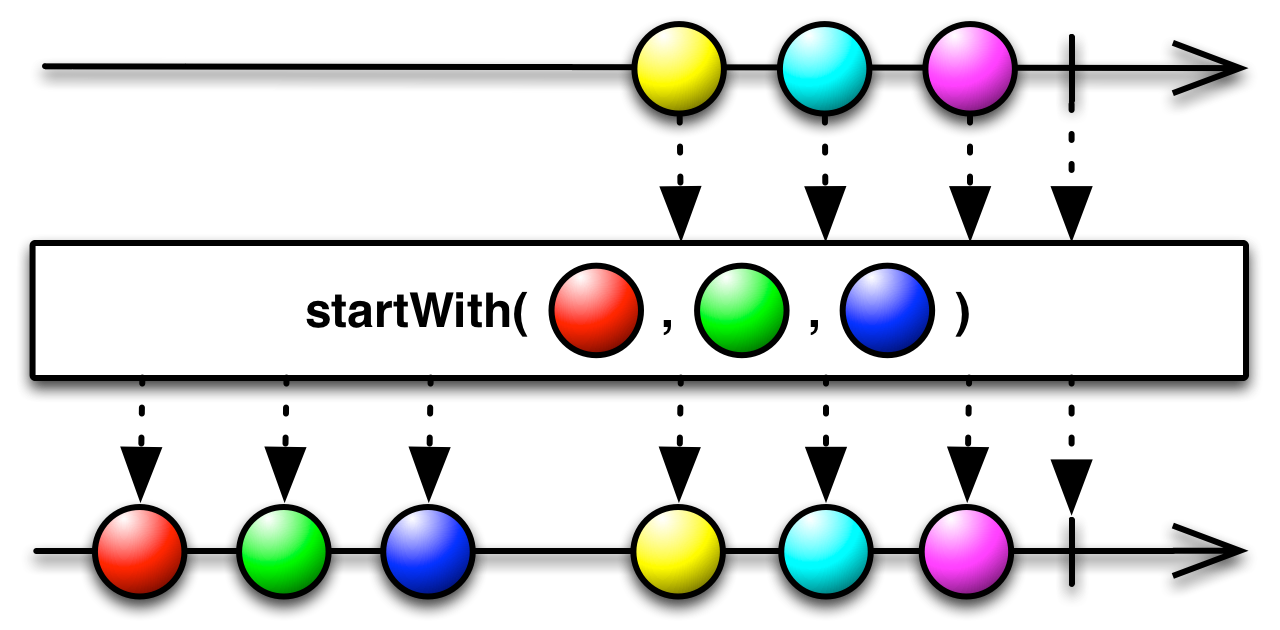
#startWith Source
startWith :: forall f a. Functor f => a -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits the item given before
it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
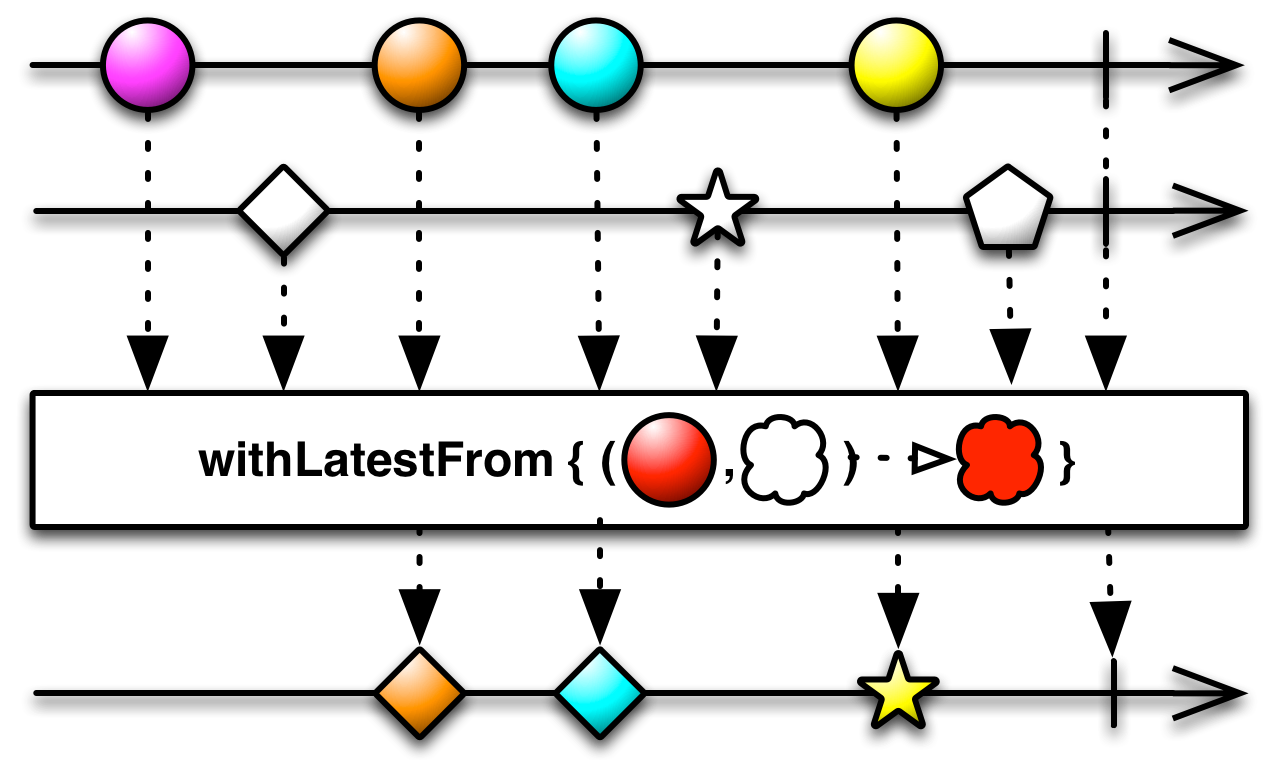
#withLatestFrom Source
withLatestFrom :: forall f c b a. Apply f => (a -> b -> c) -> ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f cCombines each value from the source Observables using a project function to
determine the value to be emitted on the output
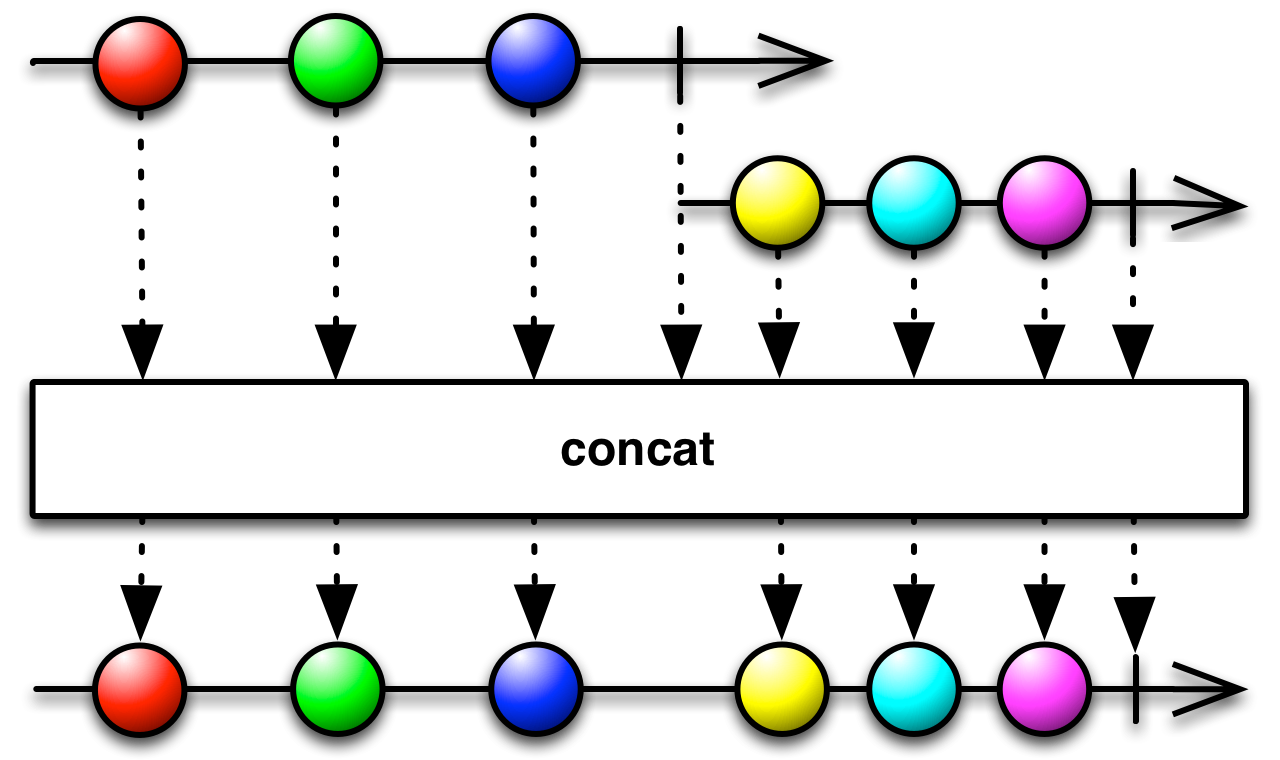
#concat Source
concat :: forall f a. Apply f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aConcatenates two Observables together by sequentially emitting their values, one Observable after the other.
#switchMapTo Source
switchMapTo :: forall f b a. Apply f => ObservableT f b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f bIt's like switchMap, but maps each value to the same inner ObservableImpl.
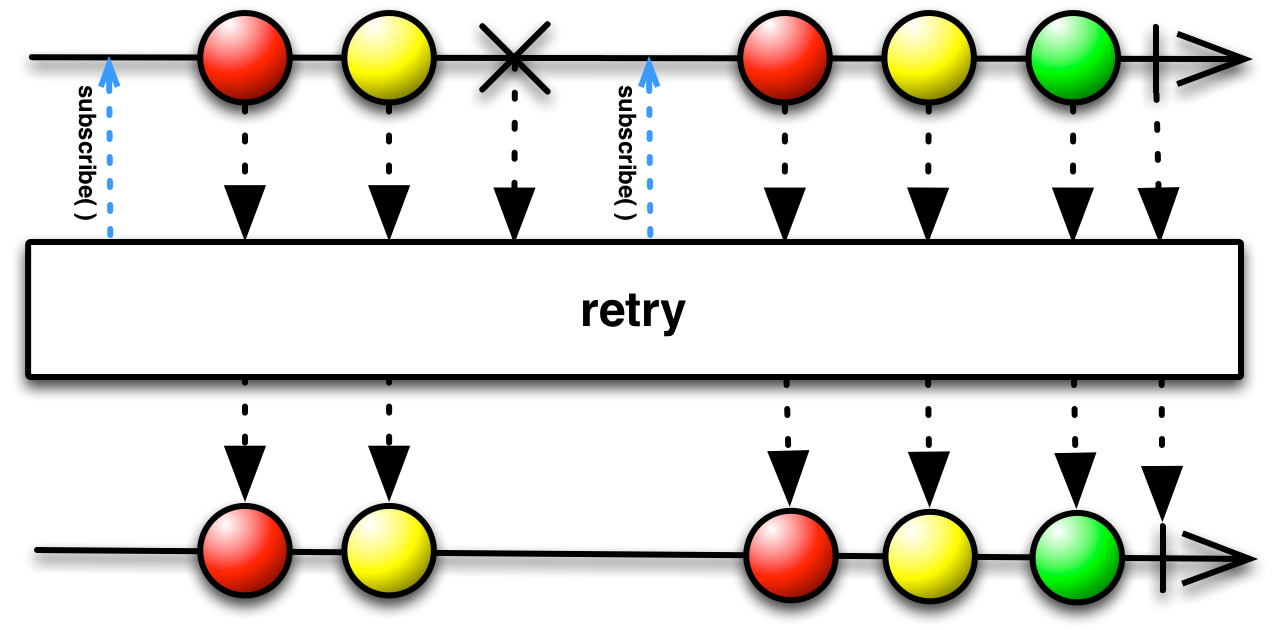
#retry Source
retry :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aIf the source Observable calls error, this method will resubscribe to the
source Observable n times rather than propagating the error call.
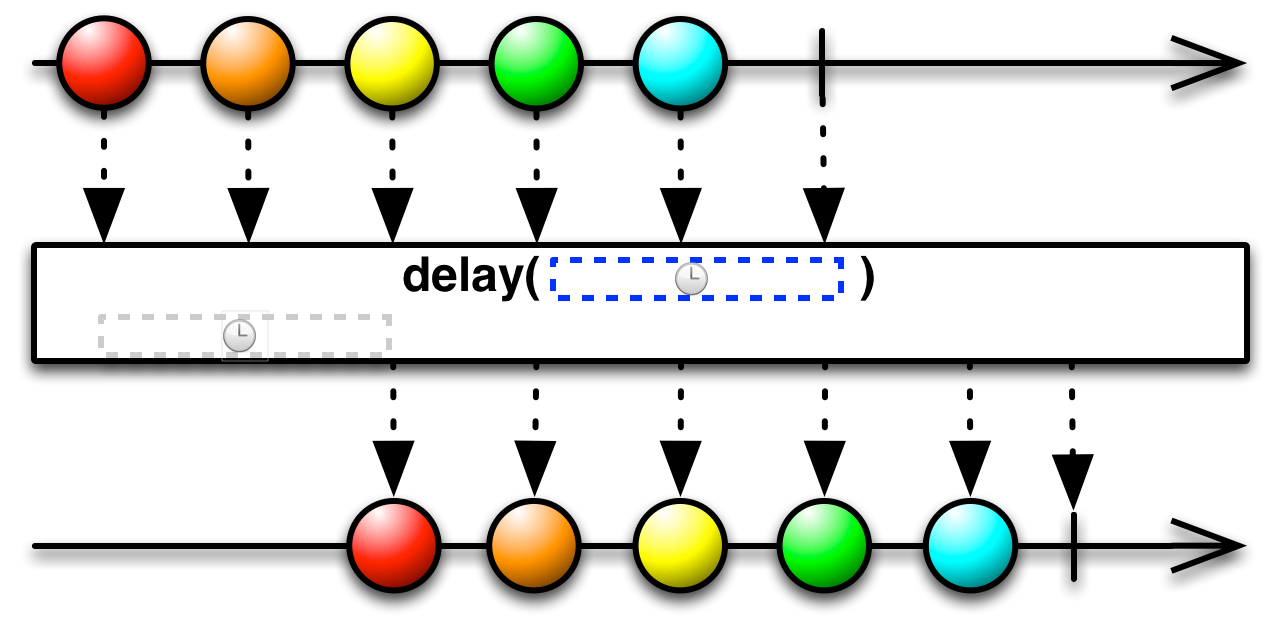
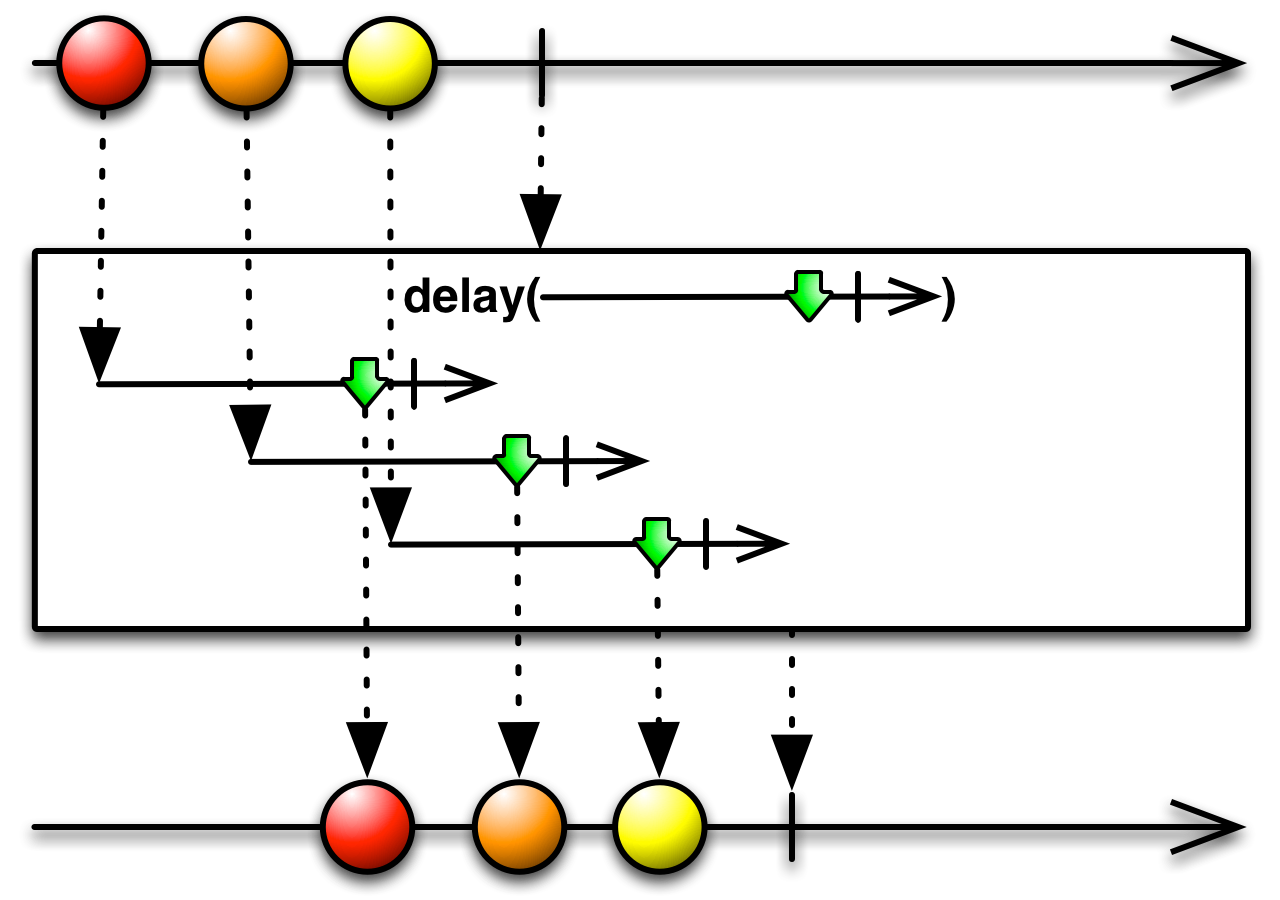
#delay Source
delay :: forall f a. Functor f => Int -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aTime shifts each item by some specified amount of milliseconds.
#defaultIfEmpty Source
defaultIfEmpty :: forall f a. Functor f => a -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.

takes a defaultValue which is the item to emit if the source Observable emits no items.
returns an Observable that emits either the specified default item if the source Observable emits no items, or the items emitted by the source Observable
#every Source
every :: forall f a. Functor f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f BooleanDetermines whether all elements of an observable sequence satisfy a condition. Returns an observable sequence containing a single element determining whether all elements in the source sequence pass the test in the specified predicate.
#isEmpty Source
isEmpty :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f BooleanTests whether this Observable emits no elements.
returns an Observable emitting one single Boolean, which is true if this Observable
emits no elements, and false otherwise.
#first Source
first :: forall f a. Functor f => (a -> Boolean) -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aReturns an Observable that emits only the first item emitted by the source Observable that satisfies the given predicate.
#count Source
count :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f IntCounts the number of emissions on the source and emits that number when the source completes.
#reduce Source
reduce :: forall f b a. Functor f => (a -> b -> b) -> b -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f bApplies an accumulator function over the source Observable, and returns the accumulated result when the source completes, given a seed value.
#observeOn Source
observeOn :: forall f a. Functor f => Scheduler -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aMakes every next call run in the new Scheduler.
#subscribeOn Source
subscribeOn :: forall f a. Functor f => Scheduler -> ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f aMakes subscription happen on a given Scheduler.
#subscribeNext Source
subscribeNext :: forall u e f a. Functor f => (a -> Eff e u) -> ObservableT f a -> f (Eff e Subscription)#subscribe Source
subscribe :: forall e f a. Functor f => Subscriber a -> ObservableT f a -> f (Eff e Subscription)Subscribing to an ObservableImpl is like calling a function, providing
next, error and completed effects to which the data will be delivered.
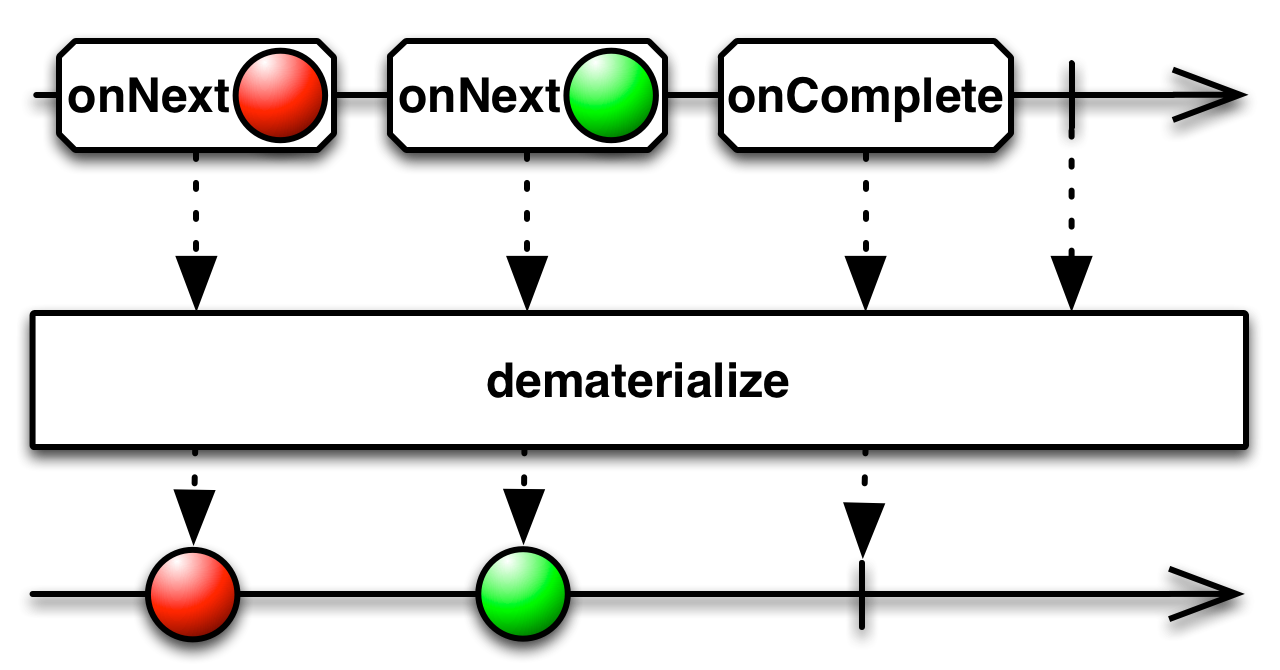
#dematerialize Source
dematerialize :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f (Notification a) -> ObservableT f aReturns an ObservableImpl that reverses the effect of materialize by
Notification objects emitted by the source ObservableImpl into the items
or notifications they represent.
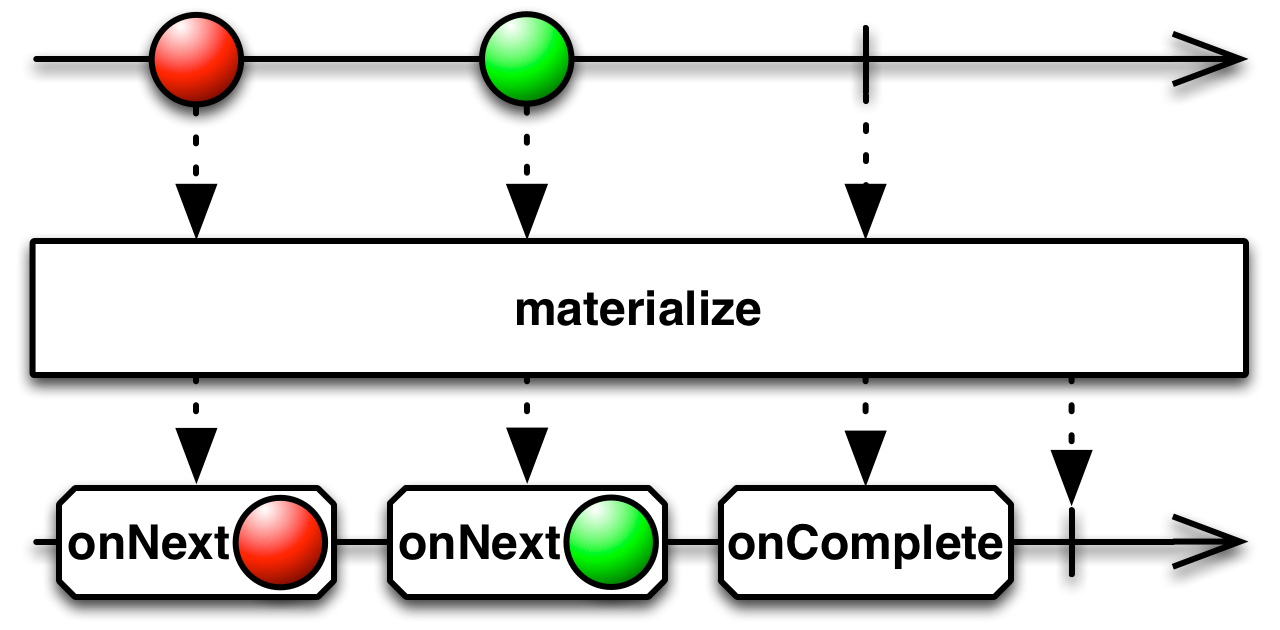
#materialize Source
materialize :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (Notification a)Turns all of the notifications from a source ObservableImpl into onNext emissions,
and marks them with their original notification types within Notification objects.
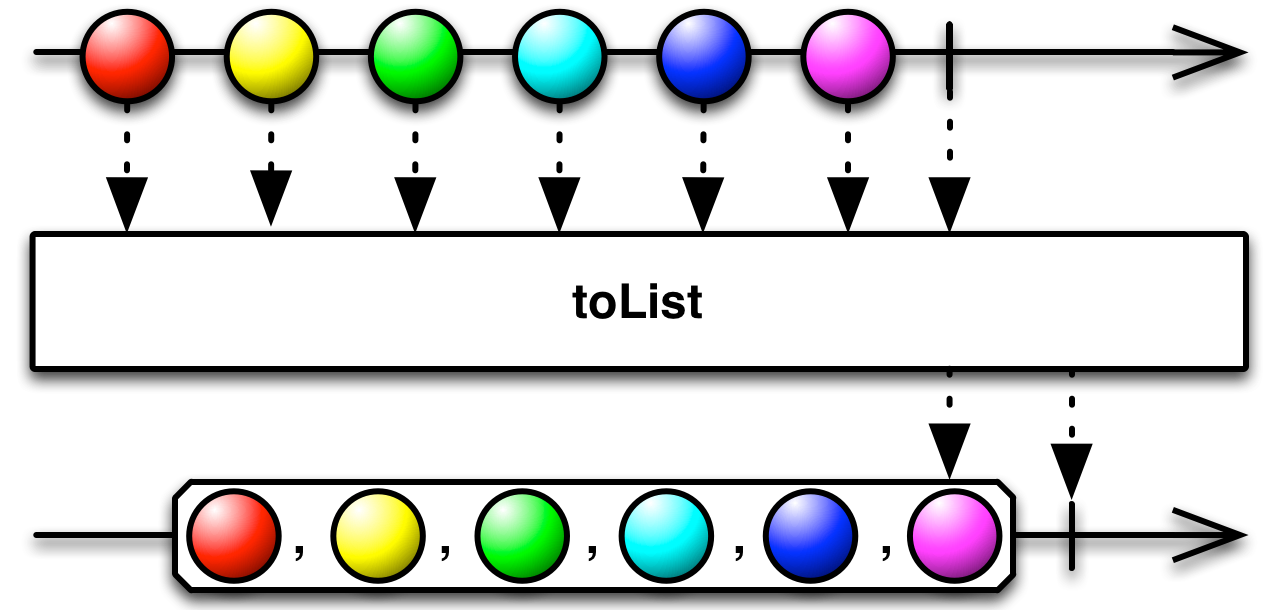
#toArray Source
toArray :: forall f a. Functor f => ObservableT f a -> ObservableT f (Array a)Returns an ObservableImpl that emits a single item, a list composed of all the items emitted by the source ObservableImpl.
#unwrapEff Source
unwrapEff :: forall a e. Observable (Eff e a) -> ObservableT (Eff e) a#audit Source
audit :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable aIt's like auditTime, but the silencing duration is determined by a second ObservableImpl.

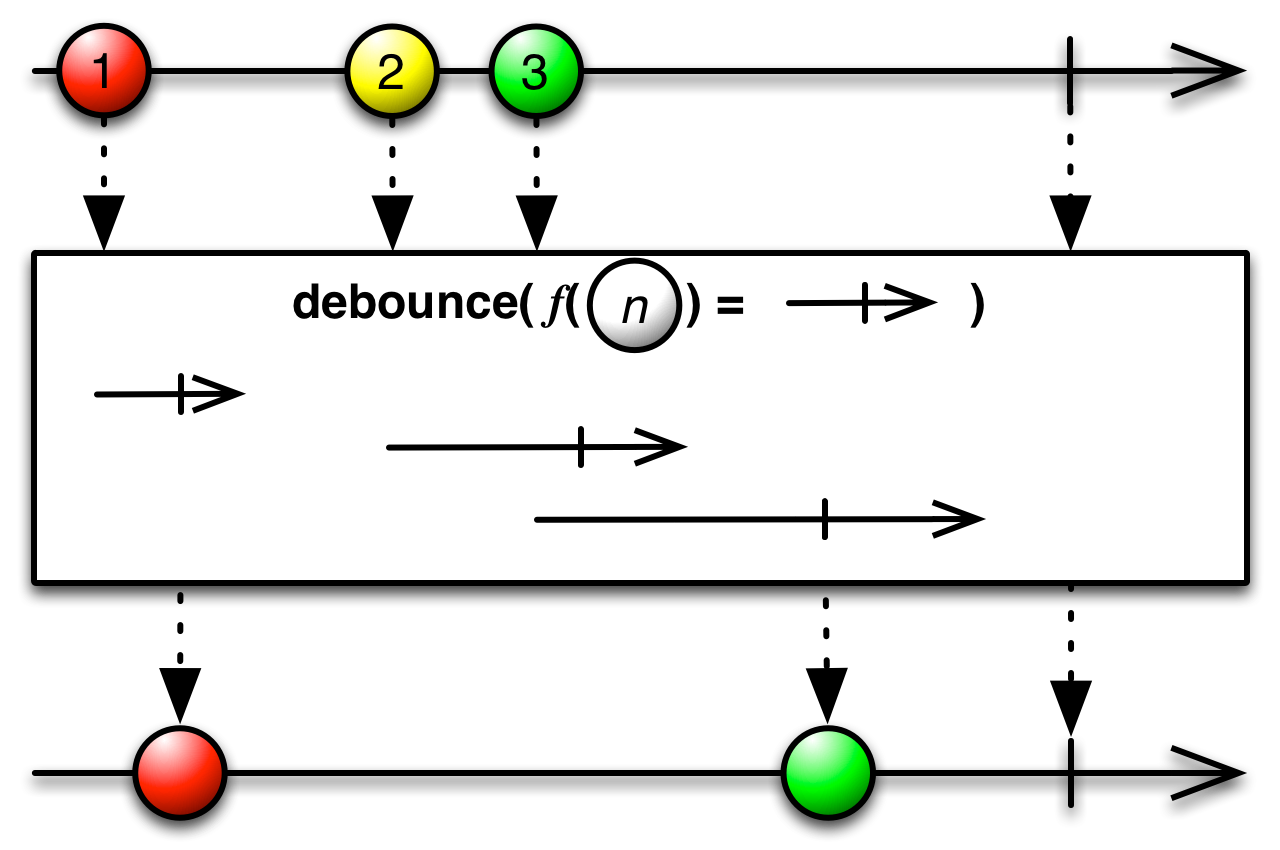
#debounce Source
debounce :: forall a. (a -> Observable Int) -> Observable a -> Observable aIt's like debounceTime, but the time span of emission silence is determined
by a second ObservableImpl. Allows for a variable debounce rate.
#bufferWhen Source
bufferWhen :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable (Array a)Collects values from the past as an array. When it starts collecting values,
it calls a function that returns an ObservableImpl that emits to close the
buffer and restart collecting.

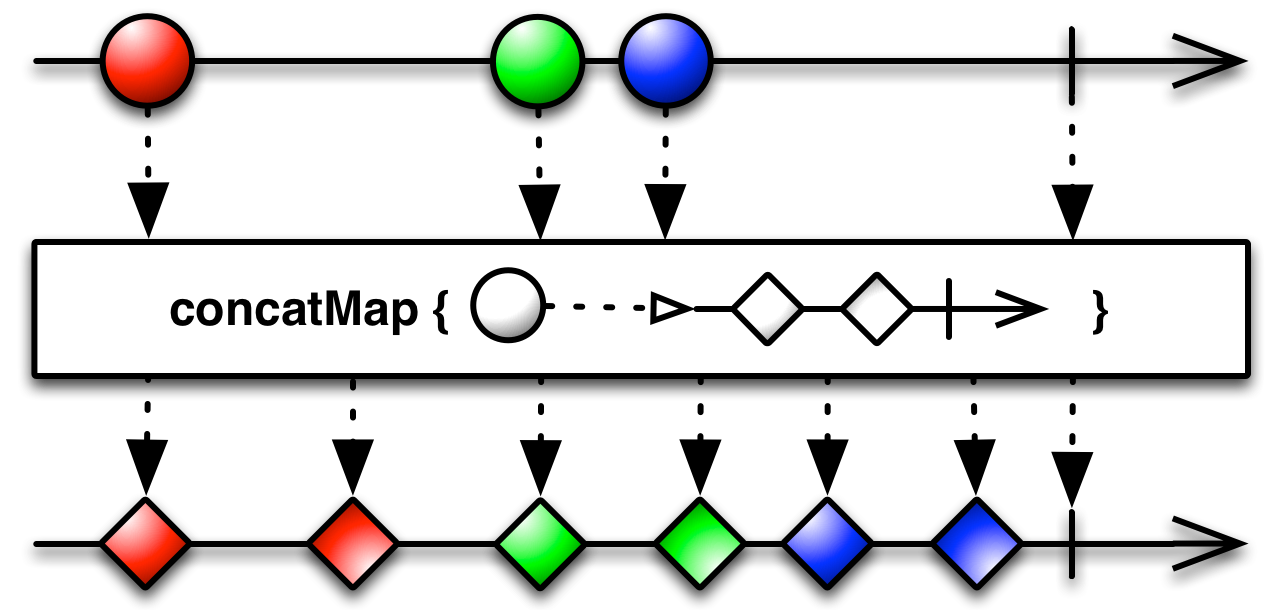
#concatMap Source
concatMap :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable bEquivalent to mergeMap (a.k.a, >>=) EXCEPT that, unlike mergeMap,
the next bind will not run until the ObservableImpl generated by the projection function (arg2)
completes. That is, composition is sequential, not concurrent.
Warning: if source values arrive endlessly and faster than their corresponding
inner ObservableImpls can complete, it will result in memory issues as inner
ObservableImpls amass in an unbounded buffer waiting for their turn to be subscribed to.
#exhaustMap Source
exhaustMap :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable bIt's Like concatMap (a.k.a, >>=) EXCEPT that it ignores every new projected
ObservableImpl if the previous projected ObservableImpl has not yet completed.

#expand Source
expand :: forall a. (a -> Observable a) -> Observable a -> Observable aIt's similar to mergeMap, but applies the projection function to every source value as well as every output value. It's recursive.
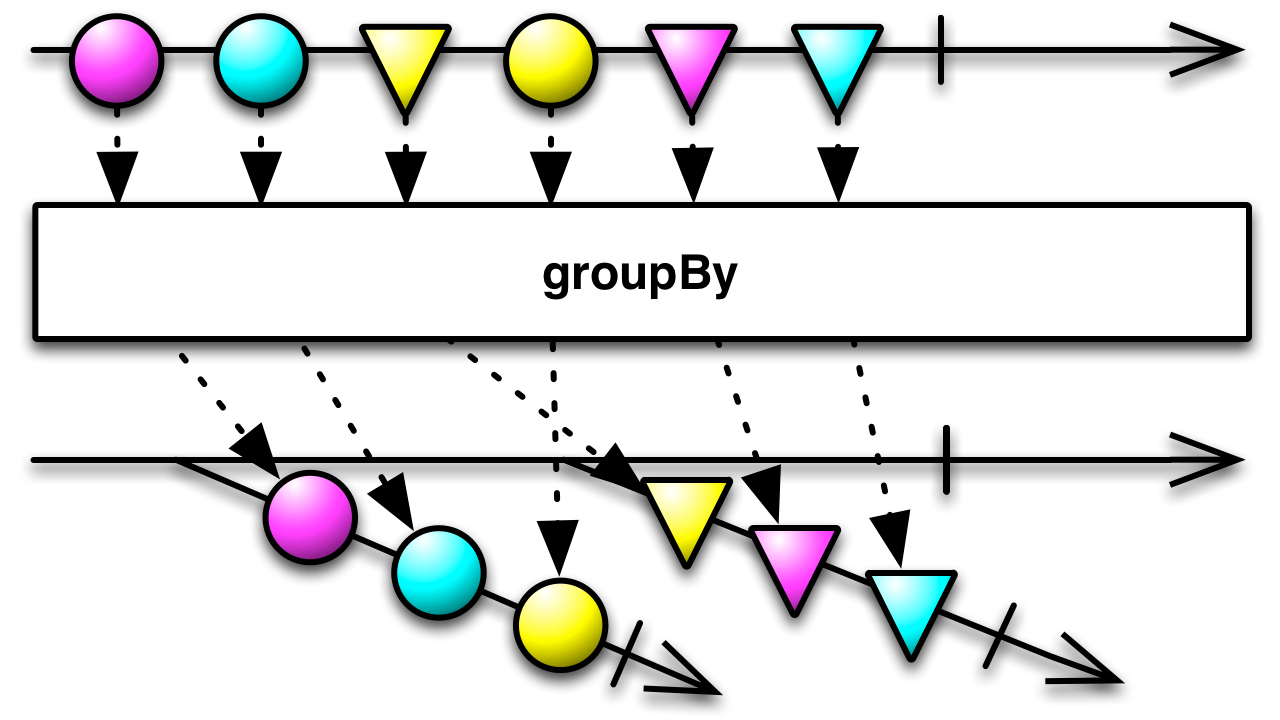
#groupBy Source
groupBy :: forall b a. (a -> b) -> Observable a -> Observable (Observable a)Groups the items emitted by an ObservableImpl (arg2) according to the value
returned by the grouping function (arg1). Each group becomes its own
ObservableImpl.
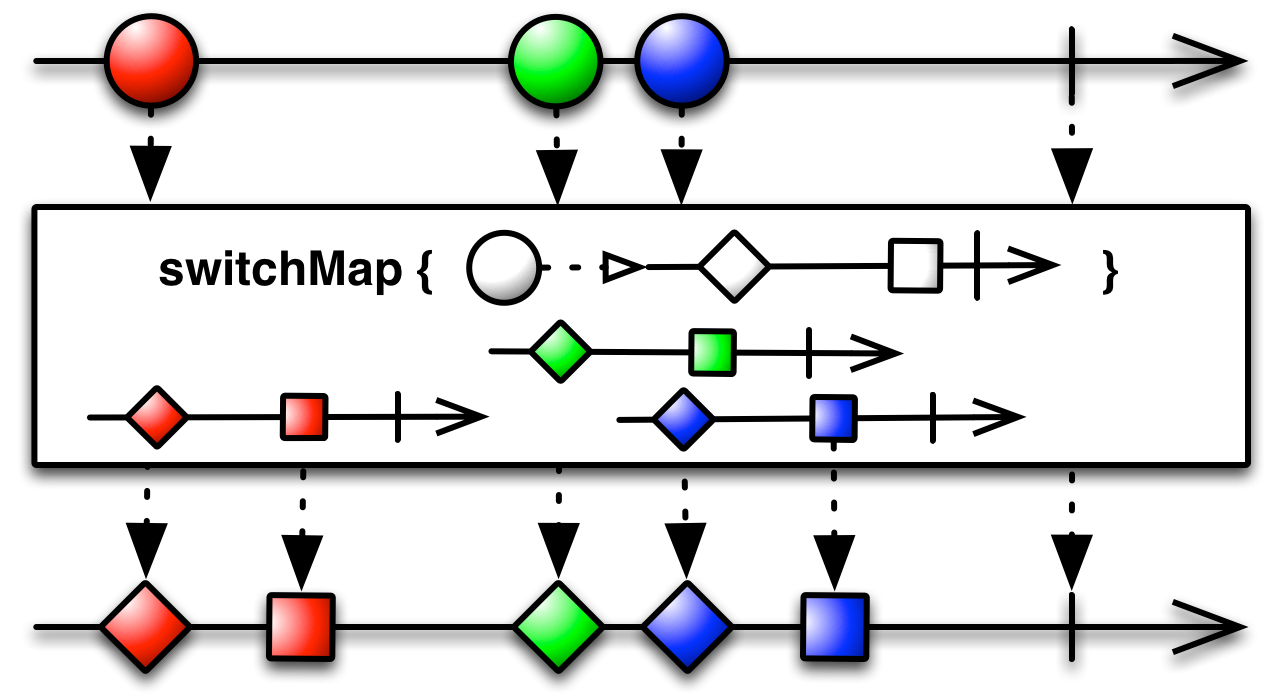
#switchMap Source
switchMap :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable bProjects each source value to an ObservableImpl which is merged in the output
ObservableImpl, emitting values only from the most recently projected ObservableImpl.

#delayWhen Source
delayWhen :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable aDelays the emission of items from the source ObservableImpl by a given time
span determined by the emissions of another ObservableImpl.
#concatAll Source
concatAll :: forall a. Observable (Observable a) -> Observable aConverts a higher-order ObservableImpl into a first-order ObservableImpl by concatenating the inner ObservableImpls in order.

#mergeAll Source
mergeAll :: forall a. Observable (Observable a) -> Observable aConverts a higher-order ObservableImpl into a first-order ObservableImpl
which concurrently delivers all values that are emitted on the inner ObservableImpls.

#race Source
race :: forall a. Array (Observable a) -> Observable aReturns an ObservableImpl that mirrors the first source ObservableImpl to emit an item from the array of ObservableImpls.
#exhaust Source
exhaust :: forall a. Observable (Observable a) -> Observable aFlattens an Observable-of-Observable by dropping the next inner Observables
while the current inner is still executing.

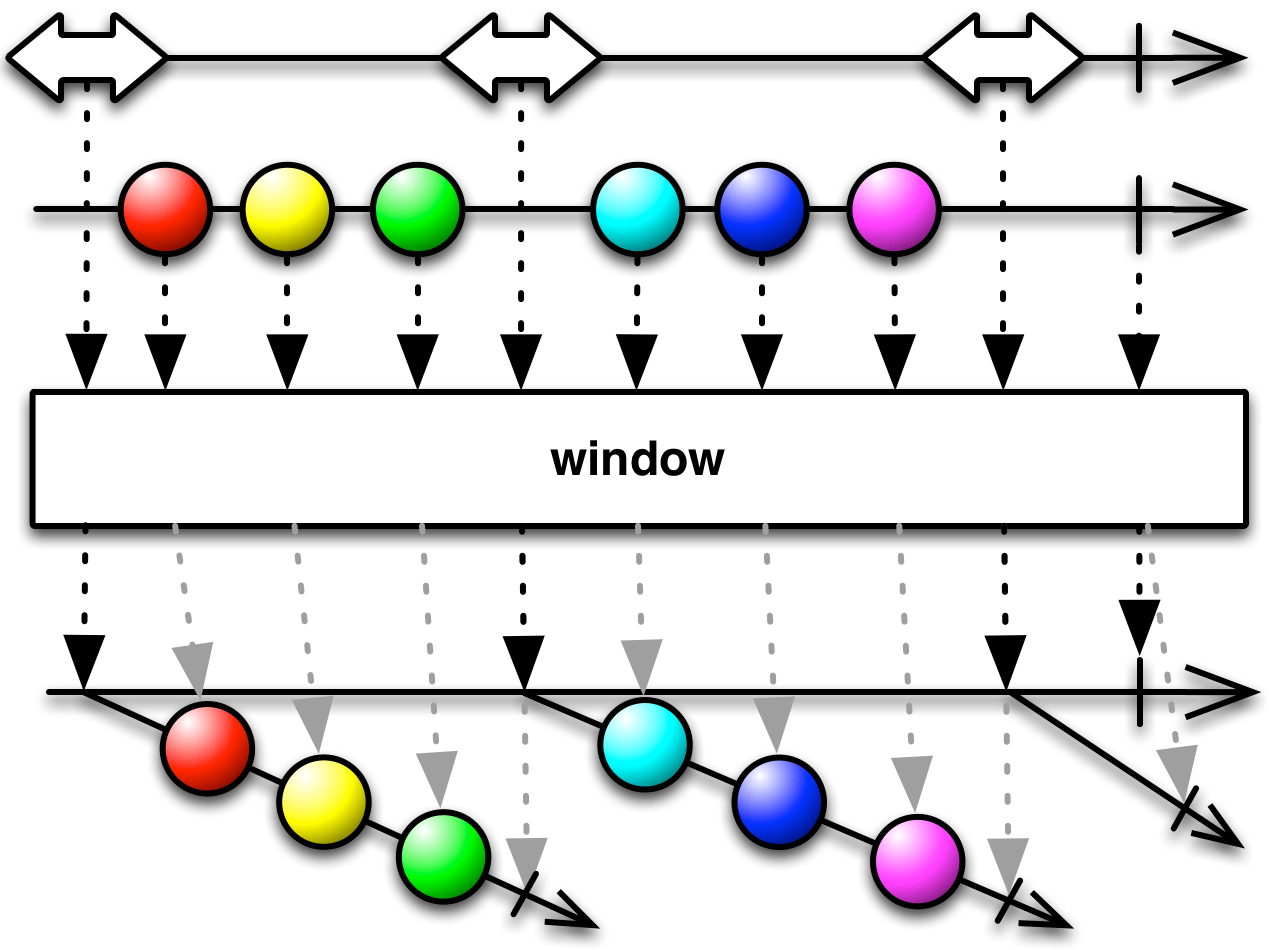
#window Source
window :: forall b a. Observable b -> Observable a -> Observable (Observable a)It's like buffer, but emits a nested ObservableImpl instead of an array.
#windowCount Source
windowCount :: forall a. Int -> Int -> Observable a -> Observable (Observable a)It's like bufferCount, but emits a nested ObservableImpl instead of an array.
#windowTime Source
windowTime :: forall a. Int -> Int -> Observable a -> Observable (Observable a)It's like bufferTime, but emits a nested ObservableImpl instead of an array, and it doesn't take a maximum size parameter. arg1 is how long to buffer items into a new ObservableImpl, arg2 is the when the next buffer should begin, and arg3 is the source ObservableImpl.
#throttle Source
throttle :: forall b a. (a -> Observable b) -> Observable a -> Observable aIt's like throttleTime, but the silencing duration is determined by a second ObservableImpl.

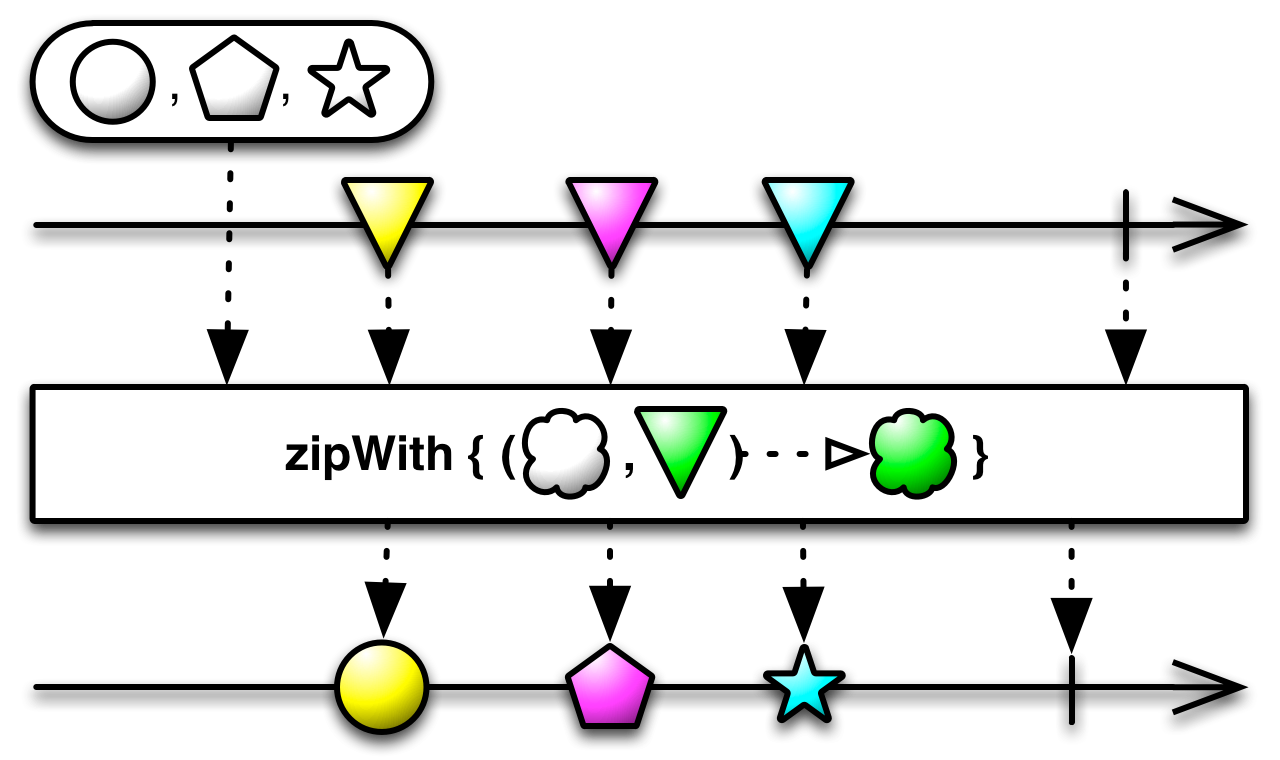
#zip Source
zip :: forall a. Array (Observable a) -> Observable (Array a)Waits for each ObservableImpl to emit a value. Once this occurs, all values
with the corresponding index will be emitted. This will continue until at
least one inner ObservableImpl completes.
#catch Source
catch :: forall a. Observable a -> (Error -> Observable a) -> Observable a